CAT Tools Overview
This post provides a quick overview of computer-assisted translation (CAT) systems.
PREVIOUS POST < || > NEXT POST
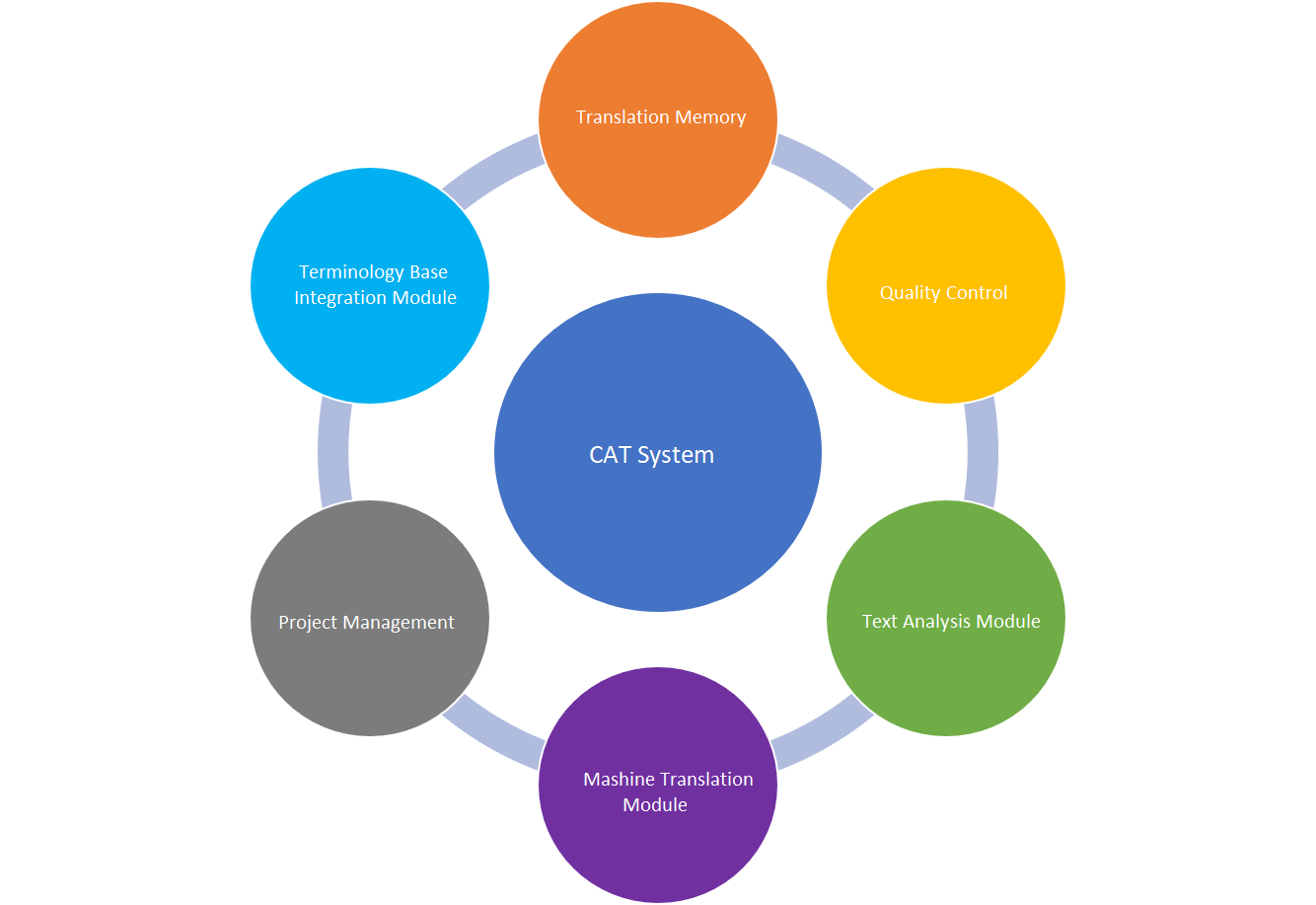
CAT tools are used to translate texts from one language to another more quickly and efficiently. The core of these systems is a translation memory that stores the source text and its translated equivalent. When a new text segment is translated, the translation memory is checked for similar and identical segments and found matches are offered to the translator for further use. The translator can apply the text without making changes to it or adjust it as needed.
In addition to the translation memory, a CAT system usually has the following built-in components:
- Editor for translating and editing texts
- Module for integrating terminology databases
- Tools for checking and evaluating translation quality (e.g., spelling and grammar check)
- Module for counting words and analyzing the translated text
- Module for comparing source and translated texts and creating a new translation memory out of them
- Modules/filters for exchanging data with other programs (e.g., Microsoft Office)
- Modules for communicating with machine translation tools
- Module for managing translation projects
Some of these functions are discussed in more detail in the following posts.
Benefits
CAT tools have many advantages as compared to manual translation, for example:
- Reducing translation time and costs (up to 40-50%)
- Ensuring consistency of style and terminology through the use of translation and terminology databases
- Improving translations quality
PREVIOUS POST < || > NEXT POST