Collaborating on a project in GitHub
This post provides information on how to collaborate on a project in GitHub using the so-called fork and pull model.
Prerequisites
In the following, we assume that you have successfully performed all preparatory steps:
- Installed and configured Git on your local computer.
- Created an account in GitHub.
- Set up authentication to GitHub from Git.
- Checked that you can access the repository you want to collaborate on and that the owner of this repository permits forking.
Configuration steps
The workflow in the fork and pull model includes completing the following steps:
- Logging in to your GitHub user account.
-
Navigating to the repository you want to collaborate on. This repository is referred to as the original one.
-
Forking the original repository to your user account. By forking, you create a copy of this repository that you can manage. You can make changes to your fork without affecting the original repository. To create a fork, click the Fork button in the top-right corner of the project's page.

- Creating a local clone of your fork by following the steps below:
- Navigate to your fork in GitHub.
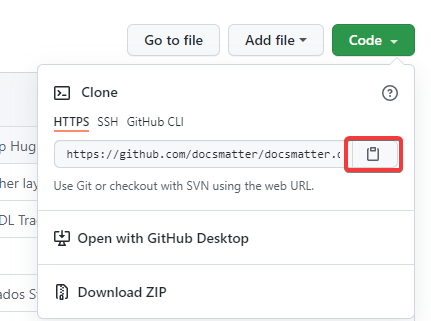
- Click on the green Code button.
- In the opened window, make sure that the HTTPS tab is selected and click on the copy icon.
-
In Git Bash (or another Git client), go to the directory where you want to create the local clone of your fork.
-
Enter the following command and press Enter:
~> git clone https://github.com/[YOUR-USERNAME]/[YOUR-FORK-NAME]
-
Configure Git to sync your fork with the original repository:
~> git remote add upstream https://github.com/[REPOSITORY-OWNER-USERNAME]/[ORIGINAL-REPOSITORY-NAME] -
Check that the original (upstream) repository has been successfully configured for your fork:
~> git remote -v origin https://github.com/[YOUR-USERNAME]/[YOUR-FORK-NAME] (fetch) origin https://github.com/[YOUR-USERNAME]/[YOUR-FORK-NAME] (push) upstream https://github.com/[REPOSITORY-OWNER-USERNAME]/[ORIGINAL-REPOSITORY-NAME] (fetch) upstream https://github.com/[REPOSITORY-OWNER-USERNAME]/[ORIGINAL-REPOSITORY-NAME] (push)
The name of the original repository must be specified in both upstream fields.
Collaborating on the original repository
Once you've performed the configuration steps above, you can start collaborating on the original repository. As a rule, your workflow will look like the following:
-
Checking the upstream branch for updates:
~> git fetch upstream -
Checking out your fork's local default branch:
~> git checkout main -
Merging the changes from the upstream branch:
~> git merge upstream/main -
Making the desired changes to the content (e.g., creating a new blog post).
-
Committing your changes to the local Git repository.
-
Pushing the changes to the fork on GitHub:
~> git push -
Creating a pull request on GitHub from the fork.
After that, the owner of the original repository can review and approve your pull request, thus merging your changes to the original project.